Introduction:
In today’s fast-paced and ever-evolving digital world, maintaining the security of sensitive data is more important than ever. One of the most vital aspects of a modern cybersecurity operation is compliance with industry regulations. As a Security Operations Center (SOC), especially those offering managed SOC services, your role isn’t just to keep systems secure – it’s also to ensure that your clients meet the necessary compliance standards required by law and industry best practices. But with a landscape constantly shifting due to new regulations, how do you know which compliance standards your SOC should be focused on? This blog will take a deep dive into the compliance standards your SOC should be helping clients meet, keeping them secure, efficient, and fully aligned with regulatory expectations.
Understanding Compliance in the Context of Cybersecurity
Before diving into specific compliance standards, it’s essential to understand why compliance is a top priority in the cybersecurity space. For any business, cybersecurity isn’t just about protecting data – it’s also about ensuring that the business operates legally and ethically. Compliance standards help businesses establish and enforce the right frameworks, ensuring that their security practices align with industry regulations, mitigating risks, and avoiding hefty fines.
In the context of a SOC, your primary responsibility is to ensure that your clients’ security operations meet these compliance requirements. As regulations evolve, so do the frameworks your SOC needs to follow. Let’s look at the top compliance standards that your SOC should help your clients meet.
1. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR, effective in the European Union (EU) and European Economic Area (EEA), is one of the most important data protection regulations in recent history. GDPR impacts any company that collects or processes data on individuals within the EU.
For your SOC, ensuring GDPR compliance means implementing strict data access controls, safeguarding data processing activities, and providing clear guidelines for data breach notifications. Helping clients maintain GDPR compliance also means supporting them with data encryption, privacy policies, and ensuring they can respond to data subject access requests (DSARs).
Key Elements:
Data encryption and anonymization
Regular data protection assessments
Risk-based approach to processing personal data
Notification of data breaches within 72 hours
2. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
If your SOC works with clients in the healthcare industry, understanding and supporting compliance with HIPAA is a must. HIPAA is a U.S. federal law that ensures the protection of sensitive patient data. Whether your client is a healthcare provider or a third-party service handling health-related data, HIPAA compliance is non-negotiable.
To support HIPAA compliance, your SOC needs to have secure systems for storing and transmitting health information. Encryption, access control, and regular audits are key measures to help your clients meet HIPAA’s strict standards.
Key Elements:
Encryption of electronic health records (EHRs)
Secure communication channels for healthcare information
Risk analysis and management programs
Access controls and regular training for staff handling sensitive data
3. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
The PCI DSS applies to any organization that stores, processes, or transmits credit card information. This compliance standard helps ensure that financial data is protected against breaches and fraud. For SOCs supporting businesses in the e-commerce or retail space, PCI DSS is critical.
To meet PCI DSS standards, your SOC must have systems in place to safeguard cardholder information. This means ensuring proper encryption for data in transit and at rest, implementing multi-factor authentication, and conducting regular vulnerability scans.
Key Elements:
Strong encryption of payment information
Regular penetration testing and vulnerability assessments
Multi-factor authentication for access to payment systems
Secure storage and disposal of payment data
4. Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA)
FISMA is a U.S. federal law that mandates all federal agencies and their contractors to secure information systems. While it’s primarily aimed at the public sector, private sector entities that handle government data are also required to comply. If your SOC manages any government contracts, FISMA compliance is non-negotiable.
FISMA compliance is broad and covers everything from risk management frameworks to incident response plans. For your SOC, this means having robust monitoring systems in place and ensuring that data integrity and confidentiality are always maintained.
Key Elements:
Establishment of security and privacy controls for information systems
Continuous monitoring and assessments of security controls
Risk management and incident response plans
FISMA documentation and reporting requirements
5. Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX)
SOX is another U.S. federal regulation, but it focuses on financial reporting and corporate governance. For publicly traded companies, SOX compliance is essential. The law mandates strict rules for maintaining accurate financial records, which often involves cybersecurity measures to protect financial data.
Your SOC will play an important role in ensuring that financial data is protected and that any suspicious activity is detected early. Protecting data integrity, securing financial systems, and providing reports to auditors are just a few of the responsibilities associated with SOX compliance.
Key Elements:
Protecting financial systems from cyber threats
Regular audits and internal controls to maintain data accuracy
Monitoring of systems related to financial reporting
Ensuring transparency and accountability in financial systems
6. ISO 27001: Information Security Management System (ISMS)
ISO 27001 is an international standard for managing information security. While not a law, it’s widely regarded as one of the best practices for cybersecurity management systems. For clients seeking to demonstrate a commitment to security, ISO 27001 certification is a major asset.
For your SOC, ensuring that your clients are compliant with ISO 27001 means helping them create and maintain a comprehensive information security management system. This includes everything from risk assessments to implementing controls to monitor and safeguard sensitive data.
Key Elements:
Establishing an information security management system (ISMS)
Regular risk assessments and gap analyses
Continuous monitoring and improvement of security policies
Auditing and reporting to maintain compliance
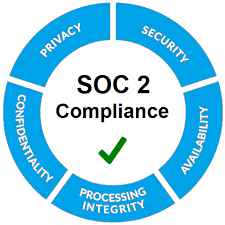
7. SOC 2 Compliance
SOC 2 compliance is particularly relevant for SaaS companies and other technology-based firms that store customer data. The standard focuses on five key areas: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
A SOC 2-compliant system ensures that your client’s systems are secure and that their customers’ data is handled appropriately. SOC 2 also requires regular audits to verify that security controls are functioning as intended.
Key Elements:
Strong access control and authentication measures
Encryption and data integrity checks
Regular auditing and reporting on data handling practices
Continuous monitoring of system performance
8. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The CCPA is a privacy law aimed at giving California residents more control over their personal data. It impacts businesses that collect personal information from California residents and that meet certain revenue thresholds or data-processing criteria.
Your SOC can help your clients comply with the CCPA by ensuring proper data access controls, providing data subjects with rights to access, delete, or opt out of the sale of their data, and ensuring timely responses to data subject requests.
Key Elements:
Data access and deletion requests from consumers
Transparency around data collection and use
Securing consumer data against unauthorized access
Providing opt-out options for data sales
Conclusion:
As a SOC, your role is far more than just keeping cyber threats at bay. It’s about ensuring that your clients stay compliant with the numerous regulations that govern data security and privacy. Whether it’s GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, or other industry-specific frameworks, compliance is crucial to building trust and maintaining secure operations.
By understanding and addressing these compliance standards, your SOC becomes an integral part of your client’s security strategy, helping them stay ahead of regulatory requirements and cybersecurity threats. Remember, every industry is unique, and staying informed about the latest regulatory changes ensures you can guide your clients with confidence.

